Basic Setup
Introduction to IDEs
- An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) serves as a comprehensive software suite designed to streamline and facilitate the software development process.
- It functions as a centralized platform, offering a range of tools and features to assist developers in coding, debugging, and deploying applications.
- The primary goal of an IDE is to enhance efficiency by providing an all-in-one solution that combines code editing, debugging, and project management within a unified interface.
An IDE typically includes:
- Code Editor: Enables developers to write, edit, and manage code efficiently with features like syntax highlighting and auto-completion.
- Debugger: Facilitates the identification and resolution of bugs and errors within the code, ensuring optimal performance.
- Compiler/Interpreter: Converts human-readable code into machine-executable instructions, allowing for code execution and testing.
- Build Automation Tools: Streamline the process of compiling source code into executable files or libraries.
- Project Management: Organizes and manages project files, facilitating collaboration and version control.
- User Interface (UI): Provides an intuitive interface for seamless navigation and accessibility to various features.
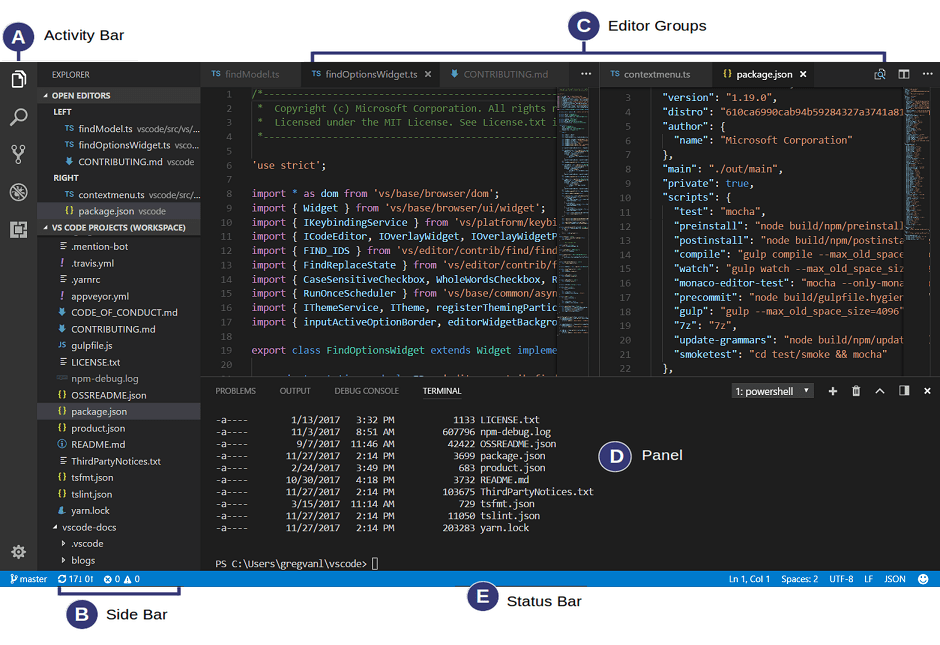
Understanding the significance of an IDE in the development workflow is crucial for establishing a productive and organized coding environment. Whether you're a novice or an experienced developer, choosing the right IDE tailored to your programming language and preferences significantly contributes to a smoother development experience.
System Requirements
Minimum system requirements for most Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) typically include:
- Processor (CPU): A multi-core processor (e.g., dual-core or quad-core) with a clock speed of 2 GHz or higher is generally recommended for optimal performance.
- RAM (Memory): At least 4 GB of RAM is a common minimum requirement. However, for more resource-intensive development tasks, 8 GB or more may be recommended.
- Storage: IDEs usually require several gigabytes of free storage space. A minimum of 10 GB of available hard disk space is a common requirement. Solid State Drives (SSDs) can significantly improve performance.
- Operating System: Most modern IDEs support multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. Ensure that your operating system is within the supported versions specified by the IDE.
- Graphics: A basic graphics card with support for a screen resolution of 1280x800 or higher is typically sufficient. Graphics performance is not usually a critical factor for IDEs.
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE): Many IDEs, especially those written in Java, require a compatible version of the Java Runtime Environment. Make sure to install the recommended JRE version.
If the minimum system requirements for an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) are not met, users may experience the following issues:
- Sluggish Performance: The IDE may run slowly and respond sluggishly, leading to a less-than-optimal coding experience. Actions like code editing, compilation, and debugging may be delayed.
- Freezing or Crashing: Insufficient system resources can cause the IDE to freeze or crash unexpectedly. This can result in loss of unsaved work and disrupt the development workflow.
- Limited Functionality: Some features of the IDE may be disabled or exhibit reduced functionality if the system lacks the necessary resources. Certain resource-intensive tools or plugins may not work correctly.
- Compilation Errors: Compiling code may fail or produce errors if the system lacks the required processing power and memory. This can impede the development and testing process.
- Unresponsiveness: Users may experience unresponsiveness when interacting with the IDE, such as delayed mouse clicks, unresponsive menus, or slow scrolling. This can hinder the overall usability of the development environment.
- Compatibility Issues: Incompatibility with specific operating system versions or hardware configurations may arise, preventing the IDE from running altogether.
To avoid these issues, it is crucial to adhere to the recommended system requirements outlined by the IDE's documentation. Users should ensure that their hardware and software configurations meet or exceed the specified minimums to guarantee a smooth and efficient development experience. Additionally, keeping the system and IDE updated with the latest patches and versions can help address compatibility issues and improve overall performance.
Recommended IDEs
Python:
-
PyCharm:
Pros: Smart code completion and analysis, Powerful navigation and refactoring tools...
Cons: Heavier on system resources, Some features are only available in the paid Professional version.
Fees: Free community edition available; Professional edition requires a subscription.
-
Visual Studio Code (VSCode):
Pros: Lightweight and fast, Extensive extension marketplace, Git integration and built-in terminal...
Cons: Some features may require extensions, Not as feature-rich as full IDEs for certain tasks.
Fees: Free and open-source.
-
Jupyter Notebooks:
Pros: Interactive and ideal for data science, Supports visualizations and documentation...
Cons: Limited for large-scale software development, Lack of robust debugging tools.
Fees: Free and open-source.
JavaScript:
-
Visual Studio Code (VSCode):
Pros: Cross-platform and highly customizable, Excellent JavaScript and TypeScript support...
Cons: May require some configuration for certain languages, Full IDE features may depend on extensions.
Fees: Free and open-source.
-
Atom:
Pros: Highly customizable and easy to use, Built-in package manager, Git integration and command palette...
Cons: Slower performance for larger projects, Not as feature-rich as some competitors.
Fees: Free and open-source.
-
WebStorm:
Pros: Dedicated IDE for web development, Smart coding assistance and error detection...
Cons: Heavier on system resources, Commercial license required.
Fees: Commercial license with a free trial available.
Java:
-
Eclipse:
Pros: Extensible and customizable, Strong support for Java EE development...
Cons: Steeper learning curve, Older-looking interface.
Fees: Free and open-source.
-
IntelliJ IDEA:
Pros: Intelligent code completion and analysis, Excellent refactoring tools...
Cons: Some advanced features are only available in the Ultimate edition, Commercial license for Ultimate edition.
Fees: Community edition is free; Ultimate edition requires a subscription.
-
NetBeans:
Pros: Simple and easy to use, Good support for Java EE and Maven, Integrated profiler...
Cons: Smaller plugin ecosystem compared to Eclipse, Less active development community.
Fees: Free and open-source.
C++:
-
Visual Studio:
Pros: Comprehensive features for C++ development, Powerful debugging tools...
Cons: Heavier on system resources, Windows-centric.
Fees: Free Community edition available; Professional and Enterprise editions require a subscription.
-
Code::Blocks:
Pros: Lightweight and fast, Cross-platform, Extensible through plugins...
Cons: Less feature-rich compared to some IDEs, Interface may feel dated.
Fees: Free and open-source.
-
CLion:
Pros: Smart code completion and navigation, Excellent support for C++11/14/17...
Cons: Commercial license required, May be resource-intensive for large projects.
Fees: Commercial license with a free trial available.
Additional Plugins
Enhance your development experience by incorporating useful plugins. Some recommended plugins include:
- Git integration for version control
- Code formatting tools for maintaining a consistent coding style
- Linters for identifying and fixing issues in your code
- Database tools for seamless interaction with databases